96 Hour Chick Embryo Serial Section
Schematic diagram of a 96-hour chick embryo + Staging Series Staging Series. About + Slime Mold. Chick Embryo Staging Stage Stage 50 53 h 55+ h 56+ h 52 64 h 64+ h 72 h 33.5 d 3.5 d Chick staging based on Hamburger V and Hamilton, HL. A series of normal stages of development of the chick embryo. J Morph 88:4962.
Chick Embryo 96 Hours Serial Sag Section Prepared Microscope Slide Limited Availability of Chick Embryo 96 Hours Serial Sag Section Prepared Microscope Slide EE12-3 Chick Embryo 96 Hours Serial Sag Section Prepared Microscope Slide 96 hr chick; serial sagital section A 10% discount applies if you order more than 10 of this item and 15% discount applies if you order more than 25 of this item. Triarch Incorporated offers superior prepared microscope slides. While we produce over 2300 different slides, we also make, and slides.
In addition, we offer affordable quality microscopes from and for less. Use coupon code SWIFT10 for an additional 10% off our already low Swift prices.
Karta navigacii ford. Sade love deluxe rar full version free software download full. Educational digital images are also available for purchase at high resolution magnifications (10x, 25x, and 100x). CS = Cross Section: So the slide shows a thin section through the transverse plane of an organism. LS = Longitudinal Section: So the slide shows a vertical section of the organism along the longest plane. WM = Whole Mount: So the slide shows an entire organism or structure, as indicated, is preserved on the slide CRT = Cross Section, Radial Section, and Tangential Section: So the slide shows sections of wood along the transverse, radial, and tangential planes. Sag = Sagittal Section: So the slide shows a thin section through the sagittal plane through the midline. Serial Sections = So the slide shows consecutive sections of the organism.
Rep = Representative Sections (Embryology): So the slide shows one section of the organism from each typical area of study. Triarch Incorporated’s name is based on a botanical slide that illustrates three ridges of xylem found in the vascular cylinder of the Ranunculus root. Our founder, George H. Conant, Ph.D., had three principles in mind: Accuracy, Service, and Dependability. He incorporated these into the Triarch logo based on the triarch vascular cylinder.
This page on the embryology in chicken relates to the following: • Whole mount preparation 72 hours, with a detail view on the development of the head () • Cross sections 72 hours; eye and heart formation ( ) Stage 72 hours Whole-mount preparation 72 hours after fertilization Information: 72 Hours after fertilization, the rotation of the embryo to the left is arrived such behind the region of the heart and only the caudal part of the embryo must twist 90 degrees. The two flexures in the head region are almost completed.
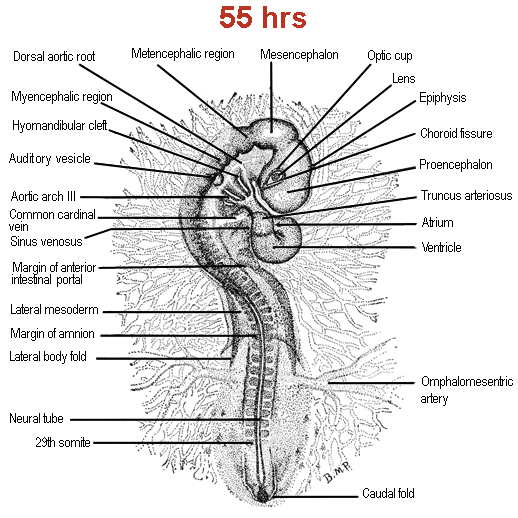
The fourth pharyngeal groove develops and the pharyngeal arches are thicker. Due to the cranial flexure, the pharyngeal region (= region of the trachea) is now located at the ventral side of the head. The fore and hind limbs at the level of the 16 th to the 20 th respectively the 27 th to the 32 th somite pairs are visible as small buds at an incubation time of about 3 days. Embryology of chicken 72 hours after fertilization: stained whole-mount preparation. 1 = Auditive (otic) vesicle, 2 = Myelencephalon, 3 = Metencephalon, 4 = Amnion, 5 = Mesencephalon, 6 = Optic vesicle + lens, 7 = Diencephalon, 8 = Epiphyse, 9 = Telencephalon, 10 = Branchial arches, 11 = Heart, 12 = Forelimb (wing) bud, 13 = Vitelline arteria/vein, 14 = Hindlimb (leg) bud, 15 = Tail Information: The development of the brain is shown at higher magnification.
The further development of the five brain vesicles (telencephalon, diencephalon, metencephalon, mesencephalon and myencephalon) in to the different head structures is clearly visible. The eye vesicles differentiate as two lateral projections of the diencephalon and come in contact with the external layer (ectoderm) to form the optic cup (neurectoderm) and the lens (ectoderm). The dorsal projection of the dieencephalon is also visible and will differentiate in to the epiphysis (epi= at the upper side). The depression at the ventral side of the diencephalon develops in to the hypophysis ( hypo= under; not visible in this fig.). The auditory vesicles develop at the level of the myencephalon.